KIA Niro: Engine Control System / Description And Operation
Description
If the Gasoline Engine Control system components (sensors, ECM, injector, etc.) fail, interruption to the fuel supply or failure to supply the proper amount of fuel for various engine operating conditions will result. The following situations may be encountered
- Engine is hard to start or does not start at all.
- Unstable idle.
- Poor driveability
If any of the above conditions are noted, first perform a routine diagnosis including the basic engine checks (ignition system malfunction, incorrect engine adjustment, etc.). Then, inspect the Gasoline Engine Control system components with the KDS.
Warning
- Before removing or installing any part, read the diagnostic trouble codes and then disconnect the negative (-) battery terminal.
- Before disconnecting the cable from battery terminal, turn the ignition switch to OFF. Removal or connection of the battery cable during engine operation or while the ignition switch is ON could cause damage to the ECM.
- The control harnesses between the ECM and heated oxygen sensor are covered by the shielded ground wires to the body in order to prevent the influence of ignition noises and radio interference. If the shielded wire is faulty, the control harness must be replaced.
- When checking the generator for the charging state, do not disconnect the positive (+) battery terminal to protect the ECM from damage due to the voltage.
- When charging the battery with the external charger, disconnect the vehicle side battery terminals to prevent damage to the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL)
EOBD
A malfunction indicator lamp illuminates to notify the driver that there is a problem with the vehicle. However, the MIL will go out automatically after 3 sequential driving cycles without the same malfunction. Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on (ON position without starting), the MIL will illuminate continuously to indicate that the MIL operates normally.
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MIL.
- Catalyst
- Fuel system
- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)
- Intake Air Temperature Sensor (IATS)
- Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor (ECTS)
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (integrated into ETC Module)
- Upstream Oxygen Sensor
- Upstream Oxygen Sensor Heater
- Downstream Oxygen Sensor
- Downstream Oxygen Sensor Heater
- Injector
- Misfire
- Crankshaft Position Sensor (CKPS)
- Camshaft Position Sensor (CMPS)
- Evaporative Emission Control System
- Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS)
- ETC Motor (integrated into ETC Module)
- Power Supply
- ECM/ PCM
- MT Encoding
- Acceleration Sensor
- MIL-on Request Signal
- Power Stage
Warning
Refer to "Inspection CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information.
NON-EOBD
A malfunction indicator lamp illuminates to notify the driver that there is a problem with the vehicle. However, the MIL will go out automatically after 3 sequential driving cycles without the same malfunction. Immediately after the ignition switch is turned on (ON position without starting), the MIL will illuminate continuously to indicate that the MIL operates normally.
Faults with the following items will illuminate the MIL
- Heated oxygen sensor (HO2S)
- Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)
- Throttle Position Sensor (TPS) (integrated into ETC Module)
- Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS)
- ETC Motor (integrated into ETC Module)
- Injectors
- ECM
Warning
Refer to "Inspection CHART FOR DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES (DTC)" for more information.
Inspection
- After turning ON the ignition key, ensure that the light illuminates for about 5 seconds and then goes out.
- If the light does not illuminate, check for an open circuit in the harness, a blown fuse or a blown bulb.
Self-Diagnosis
The ECM monitors the input/output signals (some signals at all times and the others under specified conditions). When the ECM detects an irregularity, it records the diagnostic trouble code, and outputs the signal to the Data Link connector. The diagnosis results can be read with the MIL or HI-SCAN (Pro). Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC) will remain in the ECM as long as battery power is maintained. The diagnostic trouble codes will, however, be erased when the battery terminal or ECM connector is disconnected, or by the HI-SCAN (Pro).
Warning
If a sensor connector is disconnected with the ignition switch turned on, the diagnostic trouble code (DTC) is recorded. In this case, leave the negative (-) battery terminal disconnected for 15 seconds or more until the diagnostic memory is erased.
Relationship between DTC and Driving Pattern in EOBD System
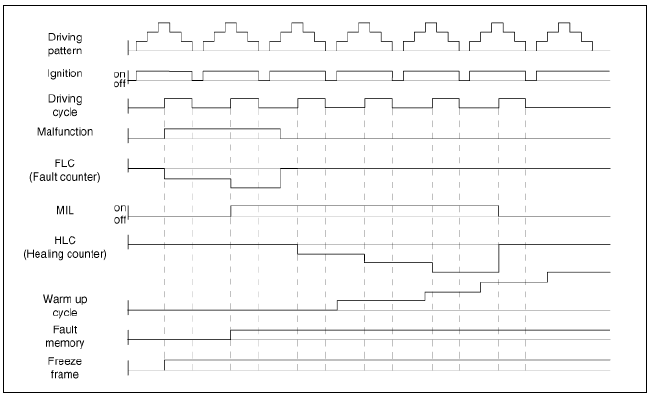
- When the same malfunction is detected and maintained during two sequential driving cycles, the MIL will automatically illuminate.
- The MIL will go out automatically if no fault is detected after 3 sequential driving cycles.
- A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) is recorded in ECM memory when a
malfunction is detected after two sequential
driving cycles.
If a misfire is detected, a DTC will be recorded, and the MIL will illuminate, immediately after a fault is first detected.
- A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) will be automatically erased from ECM memory if the same malfunction is not detected for 40 driving cycles.
Warning
- A "warm-up cycle" means sufficient vehicle operation such that the coolant temperature rises by at least 4ºC (40ºF) from engine starting and reaches a minimum temperature of 71ºC (160ºF).
- A "driving cycle" consists of engine startup, and vehicle operation beyond the beginning of closed loop operation.
READ NEXT:
 Engine Control Module (ECM) Repair procedures
Engine Control Module (ECM) Repair procedures
ECM Terminal And Input/Output signal
ECM Terminal Function
Connector (A)
Connector (K)
ECM Terminal Input/Output Signal
Connector (A)
Connector (K)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
 ETC (Electronic Throttle Control) System Repair
ETC (Electronic Throttle Control) System Repair
Inspection
Connect the KDS on the Data Link Connector (DLC).
Start the engine and measure the output voltage of TPS 1 and 2 at C.T.
and W.O.T.
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)
ETC Motor
Switch "OFF" the ignition.
Discon
 Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS)
Description
Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor (MAPS) is a speed-density type sensor
installed on the surge tank.
It senses absolute pressure of the surge tank and transfers the analog signal
proportional to the pressure
to the ECM. By using
SEE MORE:
 Removal
Removal
REMOVAL
CAUTION / NOTICE / HINT
The necessary procedures (adjustment, calibration, initialization, or registration)
that must be performed after parts are removed, installed, or replaced during the
transponder key ECU assembly removal/installat
 Clutch Actuator Motor
Clutch Actuator Motor
Remove the under cover.
(Refer to Engine Mechanical System - "Engine Room Under Cover")
Remove the front wheel guard (LH).
(Refer to Body - "Front Wheel Guard")
Disconect the clutch actuator connector (A).
Motor
Categories
- Home
- KIA Niro EV, Hybrid - Second generation - (SG2) (2021-2024) - Owner's manual
- Kia Niro - First generation - (DE) (2017-2022) - Service and Repair Manual
- Contact Us
