KIA Niro: Ignition System
Description
Ignition timing is controlled by the electronic control ignition timing
system. The standard reference
ignition timing data for the engine operating conditions are preprogrammed in
the memory of the ECM
(Engine Control Module).
The engine operating conditions (speed, load, warm-up condition, etc.) are
detected by the various
sensors. Based on these sensor signals and the ignition timing data, signals to
interrupt the primary
current are sent to the ECM. The ignition coil is activated, and timing is
controlled.
On-vehicle Inspection
Inspect ignition coil assembly and Perform spark test
- Check for DTCs.
Warning
If a DTC is present, perform Troubleshooting in accordance with the procedure for that DTC. (Refer to DTC guide)
- Check if sparks occur.
(1) Remove the engine cover.
(2) Remove the ignition coils.
(Refer to Ignition System - "Ignition Coil")
(3) Using a spark plug wrench, remove the spark plugs.
(4) Disconnect the injector extension connectors.
(5) Ground the spark plug to the engine.

(6) Check if sparks occur at each spark plug while engine is being cranked.
Warning
Do not crank the engine for more then 5 seonds.
- If sparks do not occur, perform the following test.
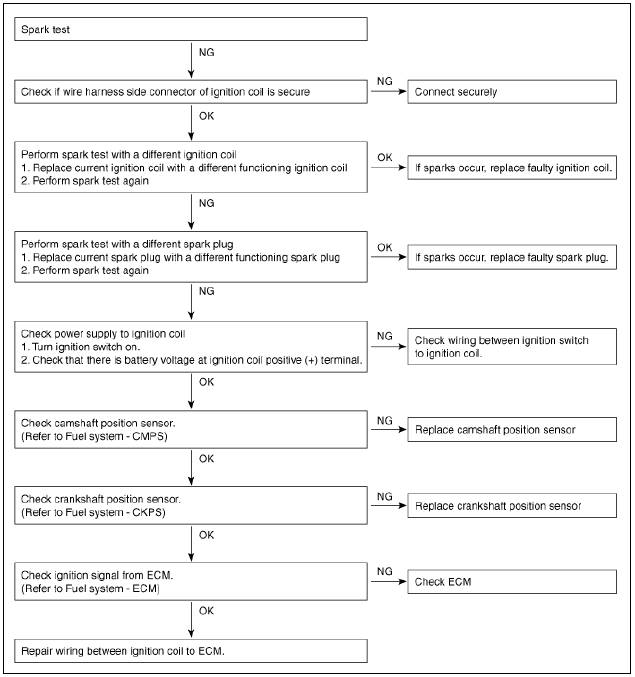
- Using a spark plug wrench, install spark plugs.
- Install the ignition coils.
- Install the engine cover.
Specification

Description
An ignition coil is an induction coil in an engine's ignition system which transforms the battery's low voltage to the high voltage needed to create an electric spark in the spark plugs to ignite the fuel. Coils have an internal resistor while others rely on a resistor wire or an external resistor to limit the current flowing into the coil from the battery 12 V supply.
Circuit Diagram

Ignition Coil Connector Terminal Function
Connector View
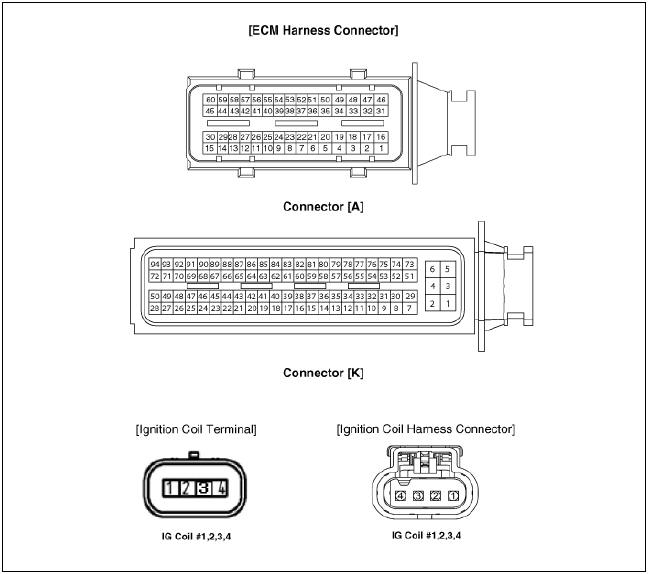
Ignition Coil Terminal Function
Ignition Coil (Cylinder #1)

Ignition Coil (Cylinder #2)
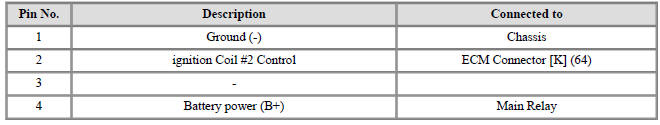
Ignition Coil (Cylinder #3)

Ignition Coil (Cylinder #4)

Troubleshooting
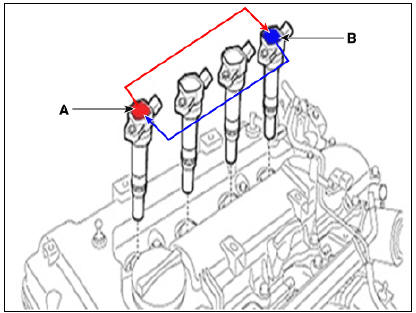
Connector assembly status test
- Remove the connector (A) and reinstall it.
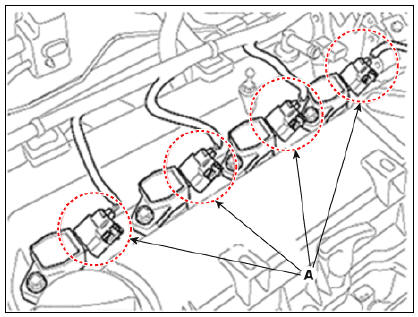

Test for changing position of each ignition coil
- Ignition coil w/ misfire code
- Ignition coil w/o misfire code
Warning
Do not move with spark plug at the same time (move the ignition coil only)

READ NEXT:
 Ignition Coil Repair procedures | Spark Plug Repair procedures
Ignition Coil Repair procedures | Spark Plug Repair procedures
Removal
Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect the battery negative (-) terminal.
Remove the engine cover.
Disconnect the ignition coil connector (A).
Remove the ignition coil (A) after loosening the mounting bolt.
I
 Emission Control System
Emission Control System
Components Location
PCV Valve
Canister
Purge Control Solenoid Valve (PCSV)
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor (FTPS)
Fuel Level Sensor (FLS)
Fuel tank air Filter
Catalytic converter (WCC)
Gasoline Particulate Filter (GPF)
PCV Valve
SEE MORE:
 How to disconnect charging connector in emergency
How to disconnect charging connector in emergency
Before disconnecting the charging
connector, make sure the doors are
unlocked. When the door is locked,
the charging connector lock system
will not allow disconnection. To prevent
charging cable theft, the
charging connector cannot be
 Fuel Filler Door / Repair Procedures | Charge Port Door Housing Assembly
Fuel Filler Door / Repair Procedures | Charge Port Door Housing Assembly
Components and components location
Fuel filler door
Fuel Filler Door / Repair Procedures
Replacement
Warning
Use a plastic panel removal tool to remove interior trim pieces without marring the surface.
Open the fuel filler door
Categories
- Home
- KIA Niro EV, Hybrid - Second generation - (SG2) (2021-2024) - Owner's manual
- Kia Niro - First generation - (DE) (2017-2022) - Service and Repair Manual
- Contact Us
