KIA Niro: Compression Pressure Inspection
Warning
If the there is lack of power, excessive oil consumption or poor fuel economy, measure the compression pressure.
- Warm up and stop the engine.
Allow the engine to warm up to normal operating temperature.
- Remove the air cleaner.
(Refer to Intake and Exhaust System - "Air Cleaner")
- Remove spark plugs.
(Refer to Engine Electrical System - "Spark Plug")
- Check cylinder compression pressure.
(1) Insert a compression gauge into the spark plug hole. If possible, place the gauge where it can be seen from inside the vehicle.

(2) Attach the KDS.
- Connect the cable of KDS to the data link connector.
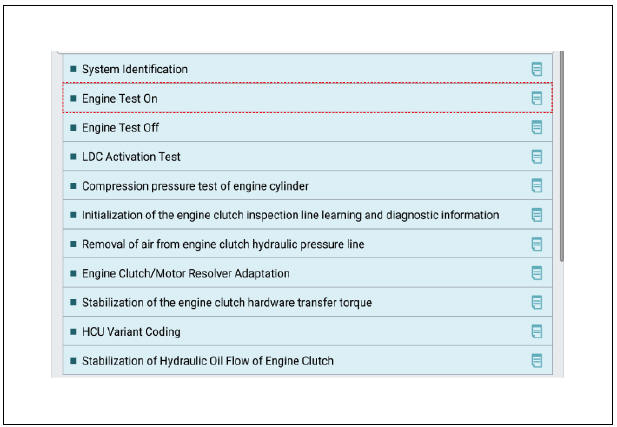
- Select the vehicle model and then the HCU system.
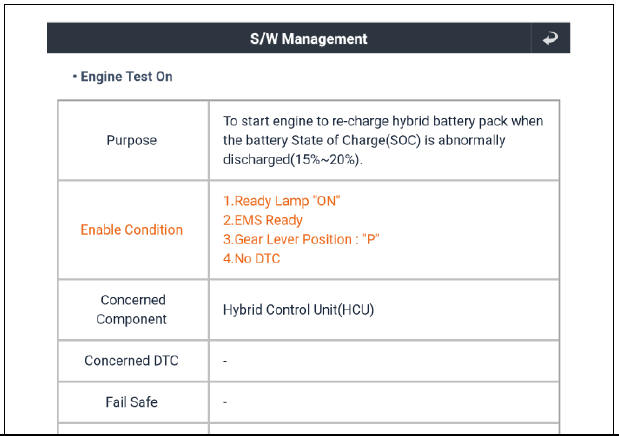
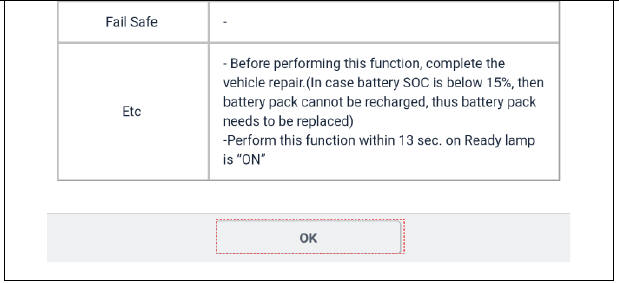
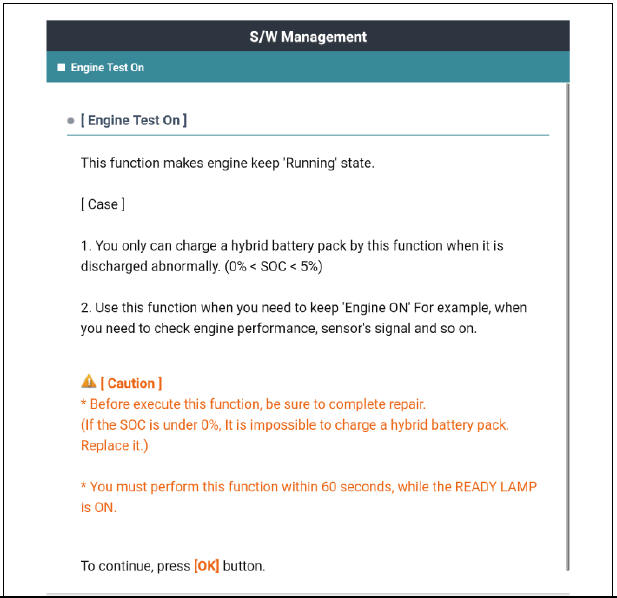
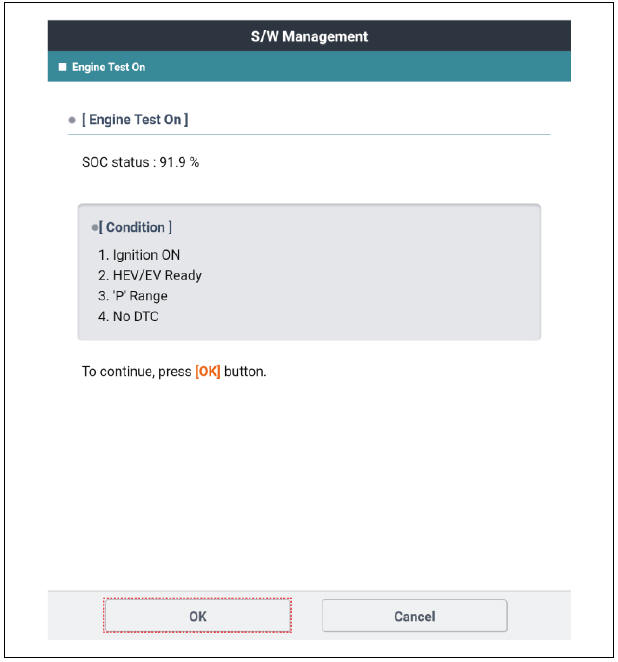
- Select the "Engine Test On". See the screens below.
(3) While cranking the engine, measure the compression pressure.
- With the Brake pedal depressed, press the Start/Stop Button (SSB) one time.
- If the engine cranks, let it crank about 8 to 10 cycles (until the gauge readings stabilizes) then press the SSB one time to stop the engine from cranking.
- If the engine does not crank on its own when the SSB is pressed, the KDS should be used to crank the engine. While in the "Engine Test On" follow the instruction on the screen.
- The "Engine Test On" will start the engine cranking. After the compression readings stabilize (8-10 cycles), press the SSB one time to stop the cranking.


(4) Repeat steps (1) through (3) for each cylinder.
Warning
Be sure ignition is in the OFF mode between each cylinder test.
This measurement must be done while the engine is still near operating temperature.
Compression pressure :
981kPa (10.0kgf/cm², 142psi) / 300 - 350rpm
Minimum pressure :
834kPa (8.5kgf/cm², 121psi) / 300 - 350rpm
Difference between each cylinder :
100kPa (1.0kgf/cm², 15psi) or less
(5) If the cylinder compression in 1 or more cylinders is low, pour a small amount of engine oil into the cylinder through the spark plug hole and repeat steps (1) through (3) for cylinders with low compression.
- If adding oil helps the compression, it is likely that the piston rings and/or cylinder bore are worn or damaged.
- If pressure stays low, a valve may be sticking or seating is improper, or there may be leakage past the gasket.
- Reinstall spark plugs.
Tightening torque : 14.7 - 24.5 N*m (1.5 - 2.5 kgf*m, 10.8 - 18.1 lb*ft)
- Install ignition coils.
Tightening torque : 9.8 - 11.8 N*m (1.0 - 1.2 kgf*m, 7.2 - 8.7 lb*ft)
- Connect the injector connectors and ignition coil connectors.
- Some DTC's may exist after the inspection test and may need to be manually cleared with KDS.
READ NEXT:
 Engine Mechanical System / Troubleshooting
Engine Mechanical System / Troubleshooting
Symptoms :
Engine misfire with abnormal internal lower engine noises
Suspected area → Remedy
Worn crankshaft bearings → Replace the crankshaft and bearings as requ
 Cooling System
Cooling System
Components
Reservoir tank
Reservoir hose & pipe
Radiator
Radiator upper hose
Radiator lower hose
Radiator upper mounting bracket (RH)
Radiator upper mounting bracket (LH)
Radiator lower mounting insulator (RH)
Radiator low
 Coolant Repair procedures
Coolant Repair procedures
Warning
Never remove the radiator cap when the engine is hot. Serious
scalding could be caused by hot fluid under
high pressure escaping from the radiator.
Warning
When pouring engine coolant, shut the relay box lid and be careful
not to spil
SEE MORE:
 Door locks outside the vehicle
Door locks outside the vehicle
Locking/unlocking with the smart key
Operation
Press the front door handle button
(driver's side).
Hazard warning lights will blink and
the chime will sound.
Locking: Once
Unlocking: Twice
Operating condition(s)
All
 Limitations of Rear Cross-Traffic
Collision-Avoidance Assist
Limitations of Rear Cross-Traffic
Collision-Avoidance Assist
Rear Cross-Traffic Collision-Avoidance
Assist may not operate properly, or it
may operate unexpectedly under the
following circumstances:
Departing from where trees or grass
are overgrown
Departing from where roads are wet
Speed of the a
Categories
- Home
- KIA Niro EV, Hybrid - Second generation - (SG2) (2021-2024) - Owner's manual
- Kia Niro - First generation - (DE) (2017-2022) - Service and Repair Manual
- Contact Us
